
eKYC Complete Guide: From Traditional to eKYC and Beyond
eKYC Complete Guide: From Traditional to eKYC and Beyond

In an era marked by innovation, interconnectedness & digital transformation, the need to build trust and security has never been more important. As the emerging need arises within businesses to protect themselves and their customers from financial crimes, identity theft & reputational damage, a powerful shield emerges: Electronic Know Your Customer.
Readers, in this blog we dive deep into KYC and EKYC. You’ll get to learn what it is, its core components, how it works, who needs it, and the future of KYC.
What is KYC?
KYC is the short form of “Know Your Customer” or sometimes “Know Your Client”. KYC is a mandatory process, specifically for banks and other financial institutions to identify their customers properly when opening an account. In other words, it is the process by which organizations make sure that the customer or client is actually who they claim they are.
Banks or other financial institutions may refuse to open an account if clients don’t meet the minimum KYC requirement.
KYC is a standard of due diligence process used by Banks, financial institutes, real estate firms, etc. to evaluate investors and clients. Apart from legal and regulatory requirements, KYC is also good business practice.
It is the standard requirement globally within the investment industry. This process is from industry regulatory bodies to protect any stakeholders involved in the transaction and it is in the best interest of any investment firm or individual financier, especially where a large sum of money is at stake.

Why KYC is important?
KYC (Know your customer) is a vital process that holds significant importance for businesses across various industries. Below are three key reasons why KYC is essential:
- Mitigating Financial Crimes & Fraud: KYC acts as a powerful curb against financial crimes such as money laundering, terrorist financing, and fraud. Through KYC businesses can identify and verify the identities of their clients, assess their risk profile, and detect any suspicious financial activities. This helps to protect businesses, the financial system, and society at large from sinister financial activities.
- Ensuring Compliance with Regulation: Compliance with regulatory requirements is a fundamental responsibility for any business. KYC plays a crucial role in meeting these obligations. Financial institutions, in particular, are subject to strict anti-money laundering (AML) and counter-terrorism financing (CTF) regulations. By implementing robust KYC processes, businesses can demonstrate their commitment to compliance, avoid legal penalties, and maintain their reputation in the industry.
- Enhancing Customer Trust and Security: KYC establishes confidence and trust among customers. When businesses implement stringent KYC procedures, customers feel assured that their personal and financial information is being protected. By verifying customer identities, businesses can prevent unauthorized account access, identity theft, and other security breaches. This fosters a secure environment for both the business and its customers, leading to stronger and more enduring relationships.
The KYC Process: Key Components of KYC
The KYC (Know Your Customer) process consists of several key components that collectively ensure thorough customer identification, due diligence, and ongoing monitoring. These components are essential for businesses to establish trust, comply with regulations, and mitigate risks. Let’s explore each component:
Customer Identification Program (CIP)
The CIP is the initial stage of the KYC process. It involves collecting and verifying the customer’s identity and basic information. This includes obtaining official identification documents such as passports or driver’s licenses, as well as gathering personal details like name, address, date of birth, and contact information. The CIP ensures that businesses have accurate and reliable information about their customers’ identities.
Customer Due Diligence (CDD)
CDD is a comprehensive assessment of the customer’s risk profile, financial behavior, and the nature of the business relationship. It involves conducting background checks and verifying the customer’s source of funds, occupation, and business activities. CDD helps businesses evaluate the potential risks associated with a customer and tailor their risk management strategies accordingly.
Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD)
EDD goes beyond standard CDD and is applied to higher-risk customers. This additional level of scrutiny involves conducting more extensive investigations and gathering more in-depth information about the customer. EDD may include researching the customer’s reputation, conducting site visits, and examining their beneficial ownership structure. EDD is crucial for mitigating risks associated with money laundering, terrorism financing, and other illicit activities.
Monitoring Transactions & Ongoing Due Diligence
KYC is not a one-time process; it requires continuous monitoring and ongoing due diligence. This involves keeping track of customer transactions and activities to identify any suspicious or unusual patterns. Regularly updating customer information, conducting periodic reviews, and reassessing risk profiles are part of the ongoing due diligence process. Monitoring ensures that businesses stay vigilant and respond promptly to any changes in customer behavior or risk profiles.
By incorporating these key components into their KYC processes, businesses can establish strong customer relationships, comply with regulations, and effectively manage risks associated with financial crimes and fraud. KYC acts as a protective shield, enabling businesses to operate safely and with integrity in today’s complex business landscape.
Digital Transformation in KYC
The era of digital transformation revolutionized the way businesses approach KYC processes. Now the traditional bureaucratic process of KYC is being replaced with innovative technologies
eKYC refers to the use of electronic methods to verify customer identities and collect various other information. Digital technologies such as online forms, and automated identity verification, simplify the KYC process. Eliminating the need to visit brick-and-mortar locations enhances customer experience.
Facial Recognition
A part of eKYC has gained prominence in the digital transformation of KYC. It allows businesses to verify the identity of the customer by comparing their facial features captured in real-time, Facial recognition algorithms analyze unique facial characteristics to establish identity verification.
Digital Account Opening
This feature of eKYC allows customers to open accounts completely online. Leveraging technologies such as online forms and fulfilling KYC requirements digitally. Completely eliminating the physical paperwork and in-person visit

eKYC vs KYC: The difference
So far we’ve figured out that KYC (Know Your Customer) is the traditional way of verifying customer identity. On the other hand, eKYC (Electronic Know Your Customer) is the digital transformation of the process where technology is leveraged to carry out customer verification.
Now that we have a high-level idea of what KYC and eKYC are, let’s dive into the difference between KYC and eKYC.
The main difference between KYC and eKYC lies in the method and approach used to verify and authenticate customer identities. Below are the three main differences between KYC and eKYC:
KYC | eKYC |
|---|---|
KYC refers to the process of verifying the identity of a customer through physical documents and in-person interactions. |
eKYC, on the other hand, utilizes electronic methods and digital technologies to verify customer identities remotely. |
It typically involves manual collection, verification, and storage of documents such as passports, driver's licenses, utility bills, and other identity proofs. |
It leverages online platforms and automated processes to collect and verify customer information, often using techniques such as facial recognition, biometric data, and secure online forms. |
KYC processes are traditionally conducted in person, requiring customers to visit a physical location, such as a bank branch, to provide their documents and complete the verification process. |
eKYC allows customers to complete the verification process remotely, eliminating the need for physical visits and paperwork. |
Traditional KYC processes often require customers to visit brick-and-mortar locations, which can be time-consuming and inconvenient. |
With eKYC, customers can complete the verification process remotely using online platforms or mobile applications, providing greater convenience and accessibility. |
Traditional KYC processes can be lengthy, involving manual document review and multiple steps, which may result in delays. |
eKYC processes are generally faster and more efficient, as they leverage automation and digital technologies for instant verification, reducing processing times significantly. |
Data accuracy in KYC depends on the manual entry and review of documents, which can be prone to human error. Physical document storage also poses security risks. |
eKYC processes minimize the risk of errors by automating data entry and verification. Secure digital platforms ensure data privacy and protection. |
Traditional KYC processes can be resource-intensive, requiring manual labor, physical storage, and administrative overheads. |
eKYC processes are scalable and cost-effective, as they leverage digital technologies to streamline operations, reduce paperwork, and minimize administrative costs. |
It’s important to note that the implementation of eKYC must comply with applicable regulations and data privacy laws to ensure the security and privacy of customer information.
In the following chart, you can see the difference between the traditional KYC and eKYC process
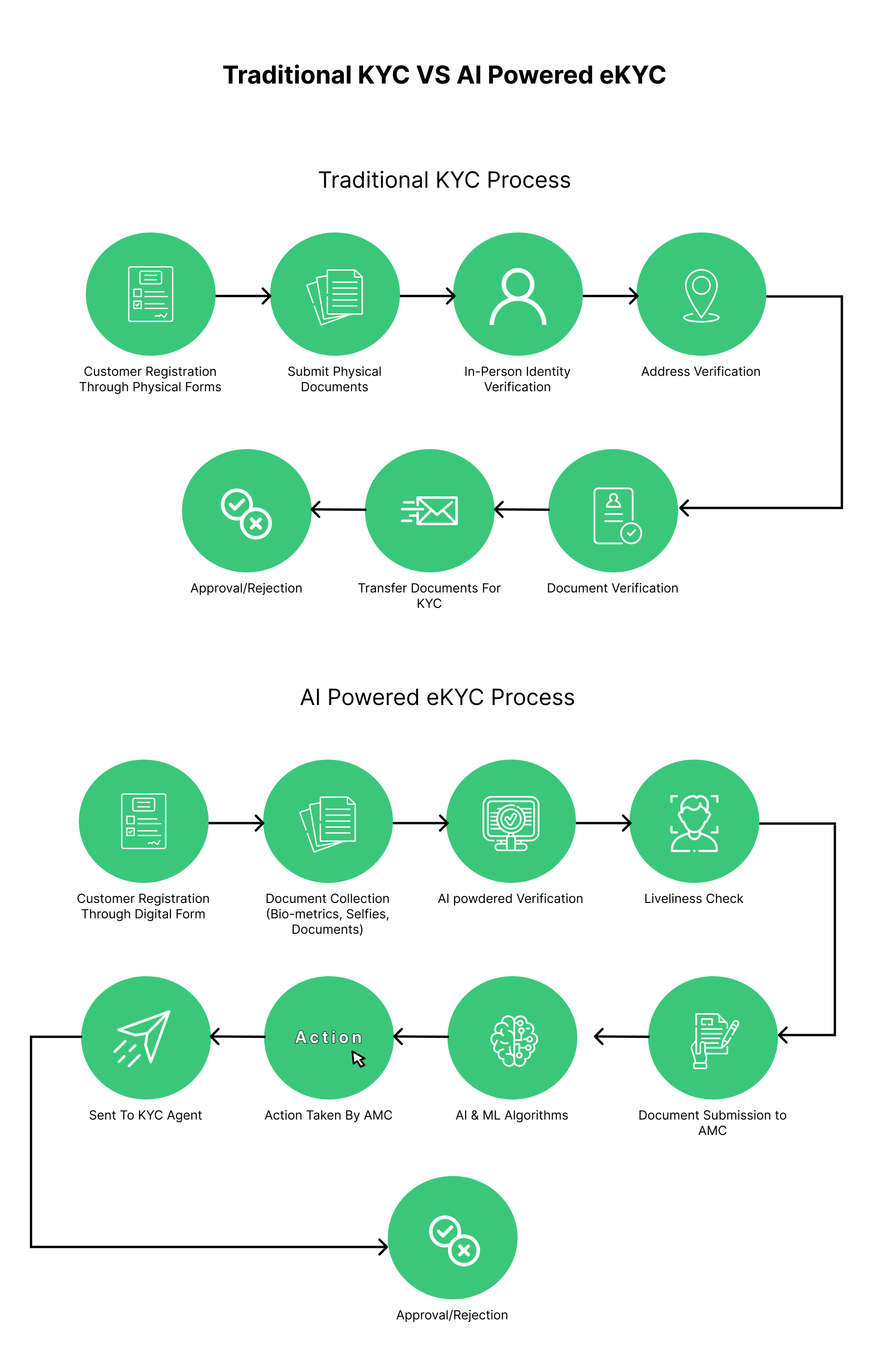
Advantages and Challenges of eKYC Implementation
Let’s get to know the advantages of implementing eKYC
- Enhanced Efficiency: eKYC streamlines the customer’s onboarding process, reducing manual intervention and paperwork. This leads to faster processing times, improved operational efficiency, and a smoother customer experience
- Cost savings: By eliminating the need for physical verification, eKYC can significantly reduce operational costs for businesses. It also reduces the need for physical infrastructure and personnel for KYC purposes.
- Improved Customer Experience: eKYC offers convenience to customers by allowing them to complete the verification process remotely, anytime, and anywhere. This eliminates the need for physical visits to branches or offices, leading to a more seamless and user-friendly onboarding experience.
- Accuracy and Data Integrity: Automated data entry and verification in eKYC reduce the chances of manual errors and discrepancies. It improves the accuracy and integrity of customer data, ensuring reliable information for compliance and risk management purposes.
- Enhanced Security: eKYC utilizes advanced technologies such as facial recognition, biometrics, and encryption to enhance security measures. This reduces the risk of identity theft, fraud, and unauthorized access to customer information.
Now that we have a good understanding of the advantages of implementing eKYC let’s get to know some of the challenges that are associated with implementing it:
- Technological Infrastructure: Implementing eKYC requires a robust technological infrastructure, including secure platforms, reliable internet connectivity, and compatibility with various devices and operating systems. Businesses need to invest in and maintain these resources to ensure a seamless eKYC process.
- Regulatory Compliance: eKYC implementation must adhere to strict regulatory requirements to ensure the privacy and security of customer data. Businesses need to stay updated with evolving regulations and ensure compliance with data protection laws and industry-specific regulations.
- Data Privacy Concerns: Collecting and storing customer data electronically raises concerns about data privacy and protection. Businesses must have stringent security measures in place to safeguard customer information from unauthorized access or data breaches.
- User Adoption and Education: Customers may have concerns or reservations about eKYC due to unfamiliarity with the process or concerns about data privacy. Educating customers about the benefits and security measures of eKYC can help address these concerns and promote user adoption.
- Integration Challenges: Integrating eKYC systems with existing IT infrastructure and legacy systems can be complex. It may require technical expertise and careful planning to ensure seamless integration and compatibility with other business processes.
Who Needs eKYC?
eKYC (Electronic Know Your Customer) is beneficial for various industries and sectors. Here are some entities that can benefit from eKYC implementation:

Banks and Financial Institutions: Banks and financial institutions can leverage eKYC to streamline customer onboarding processes, improve operational efficiency, and enhance security. eKYC enables them to verify customer identities remotely and quickly, reducing paperwork and manual processes.
Cryptocurrency Exchanges: eKYC is crucial for cryptocurrency exchanges to comply with regulatory requirements and prevent money laundering and fraud. It allows them to verify the identities of customers who want to trade cryptocurrencies, ensuring a secure and compliant environment.
Insurance Companies: Insurance companies can use eKYC to simplify the policy application and underwriting processes. By implementing eKYC, they can quickly and accurately verify customer identities, assess risks, and expedite the policy issuance process.
E-commerce Platforms: eKYC helps e-commerce platforms verify the identities of their customers, ensuring secure transactions and preventing fraudulent activities. It enables a smoother onboarding process for new customers, leading to enhanced trust and customer satisfaction.
Mobile Payment Service (MFS) Providers: eKYC is vital for mobile wallet providers who offer digital payment services. It allows them to verify the identities of users, comply with regulations, and prevent unauthorized access to mobile wallets, ensuring secure and reliable transactions.
Regulatory Landscape of KYC
Global regulations and standards:
The Fourth EU Money Laundering Directive (4AMLD) and the Fifth EU Money Laundering Directive (5AMLD): These directives outline AML and KYC obligations for European Union member states, including customer due diligence, record-keeping, and risk assessment requirements.
USA PATRIOT Act: Enacted in the United States after the 9/11 attacks, the USA PATRIOT Act introduced various AML and KYC provisions. It requires financial institutions to establish robust KYC programs and report suspicious transactions to authorities.
Financial Services Authority (FSA) Regulations: These regulations are set by various financial regulatory bodies in different countries and regions. They establish requirements for KYC compliance for financial institutions operating within their jurisdictions.
Penalties for non-compliance
The penalties for non-compliance with KYC regulations vary depending on the jurisdiction and severity of the violation. They may include:
Monetary Penalties: Financial institutions can face significant fines and monetary penalties for non-compliance with KYC regulations. The amount of the penalty can vary based on the specific violation and the regulatory body imposing the penalty.
Reputational Damage: Non-compliance can result in reputational damage for financial institutions, leading to a loss of customer trust, negative publicity, and potential loss of business opportunities.
Regulatory Sanctions: Regulatory bodies have the power to impose sanctions on non-compliant financial institutions, which can include restrictions on business operations, suspension or revocation of licenses, and limitations on future activities.
Legal Consequences: Non-compliance with KYC regulations can also lead to legal consequences, including criminal charges, civil lawsuits, and potential imprisonment for individuals involved in illegal activities.
It is essential for financial institutions to ensure robust KYC compliance to mitigate the risk of penalties, protect their reputation, and maintain the trust of regulators and customers.
The future of KYC(Know Your Customer)
The future of KYC is poised to undergo significant transformations driven by technological advancements and innovative solutions. Here are some key developments shaping the future of KYC:
Advancements in Technology and Automation: Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), robotic process automation (RPA), and natural language processing (NLP) are being integrated into KYC processes. These technologies enable automated data extraction, document verification, and risk assessment, reducing manual effort and improving efficiency.
Integration of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: AI and machine learning algorithms can enhance KYC processes by analyzing large volumes of data, identifying patterns, and detecting anomalies or suspicious activities. These technologies enable more accurate risk assessments, improved fraud detection, and enhanced customer due diligence.
Streamlining KYC Processes through Blockchain: Blockchain technology offers decentralized and immutable record-keeping, which can streamline the KYC process. It allows for secure sharing and verification of customer information across multiple entities, reducing duplication, improving data accuracy, and ensuring privacy and data protection.
Digital Identity Solutions: Digital identity solutions, such as self-sovereign identity (SSI) and decentralized identity (DID), hold the potential to transform KYC processes. These solutions enable individuals to have more control over their personal data and share only the necessary information with trusted entities, improving privacy and reducing reliance on centralized databases.
Biometric Authentication: Biometric technologies, including facial recognition, fingerprint scanning, and voice recognition, can enhance KYC processes by providing secure and convenient methods of identity verification. Biometric authentication can mitigate identity theft risks and improve the overall customer experience.
Regulatory Evolution: Regulatory frameworks around KYC are evolving to accommodate technological advancements and digital transformations. Regulatory authorities are increasingly recognizing the potential of innovative solutions to improve KYC efficiency while maintaining robust compliance standards.
Wrapping up
The future of KYC lies in leveraging technology, automation, and data-driven approaches to enhance efficiency, accuracy, and security. These advancements will not only streamline the onboarding process but also enable continuous monitoring and real-time risk management. By embracing these developments, businesses can enhance customer trust, reduce costs, and effectively combat financial crimes in an increasingly digital and interconnected world.