
Blockchain Beyond Cryptocurrency: Use Cases And Challenges
Blockchain Beyond Cryptocurrency: Use Cases And Challenges

Sadman Sakib Khan
Sadman is a marketing professional and a fervent devotee of the ever-evolving world of marketing & technology. Possessing a knack for crafting compelling narratives, Sadman passionately engages in the creation of top-tier content in close partnership with esteemed subject matter experts. During his leisure hours, he indulges in the art of musical expression, immerses himself in cultural exhibitions, watch anime, and travel.

The use of blockchain applications is more than cryptocurrency. Although the success of cryptocurrencies made it relevant.
In this post, we’ll discuss the use cases of blockchain. Also some of its challenges. But before diving into its use cases; let’s do a quick background check.
And, if you don’t know already, let’s get to know what blockchain is.
What is Blockchain?
Long story short, blockchain is a secure and transparent database system. It stores the data in blocks that are chained to one another. Allowing secure and transparent transactions.
It’s decentralized, which means there is no central controlling authority. Computers & called nodes do the heavy lifting. They confirm these transactions and add them to the digital ledger.
Blockchain is most useful in industries that need secure, and transparent record-keeping.
The History: How Blockchain Came Into Existence?
Research scientists Stuart Haber and W. Scott Stornetta first introduced blockchain in 1991. They introduced a way to mark documents with timestamps. It became difficult to change or backdate the information.
Moving forward, computer scientist, Hal Finney developed digital cash. It’s called Reusable Proof Of Work(RPoW). Early steps of creating cryptocurrency. RPoW allowed users to exchange proof-of-work tokens. It was like a ticket that proved a person has done some computational work. This made it difficult to fake these tokens.
Later on, Satoshi Nakamoto conceptualized and improved distributed blockchain. He created a unique method to add blocks. It doesn’t need signatures from trusted parties. The improvement was beneficial enough to become the backbone of all cryptocurrency. In the cryptocurrency space, it’s serving as a public ledger for all transactions.
Now that we have a brief idea of blockchain and its history. Let’s explore some of its challenges.
The Challenges Of Using Blockchain
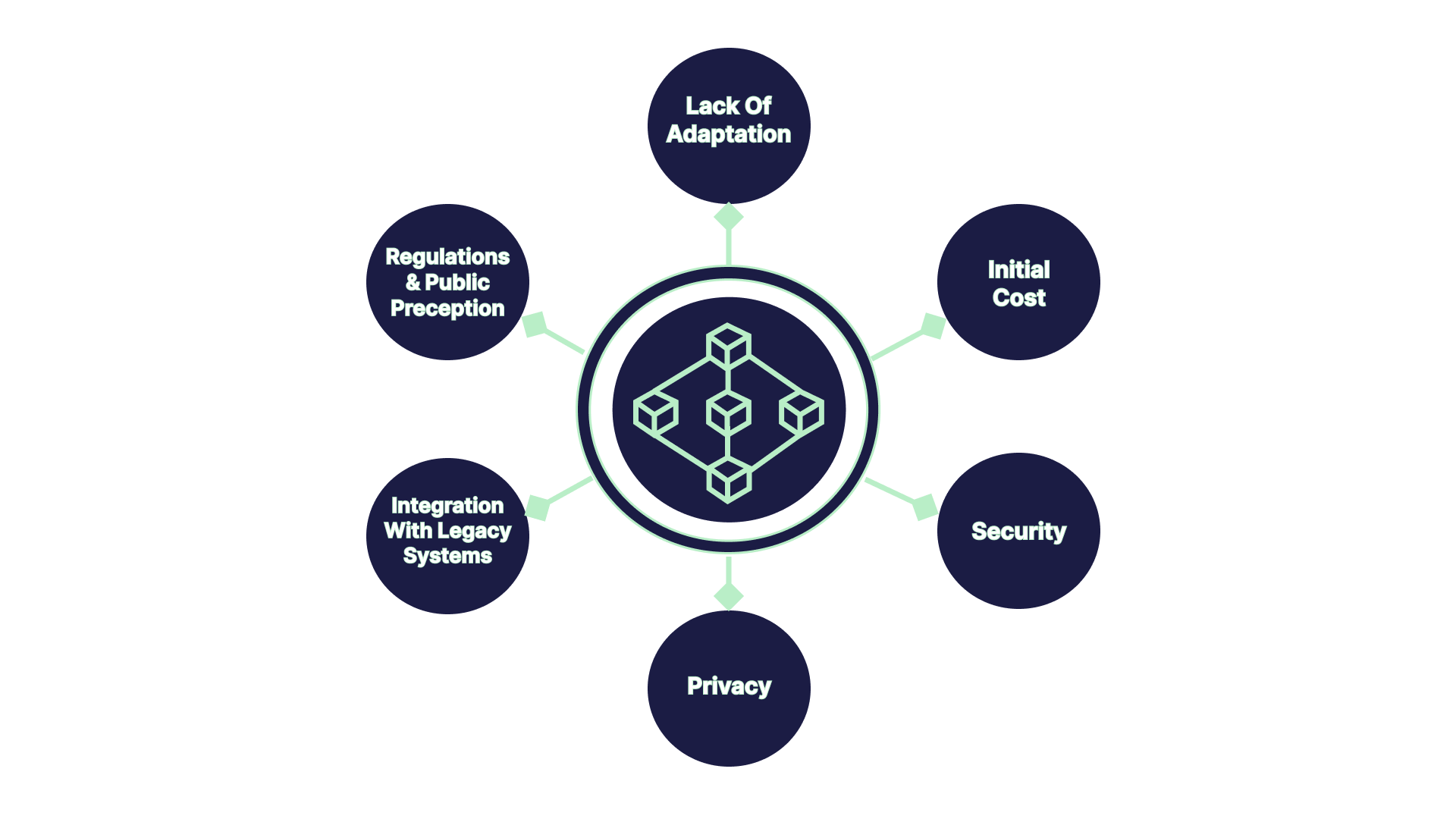
Lack Of Adaptation
Blockchain isn’t broadly accepted. APCQ discovered 29% of organizations are experimenting with or using blockchain. Blockchain works best when used across a wide network. A blockchain ecosystem needs more than just users. It needs the suppliers to join the network too. And, without broad approval blockchain will remain ineffective.
Initial Cost
Blockchain is still in its early days. And, finding skillful developers is expensive. A mining rig consists of several servers and giant computers. This consumes a lot of electricity. That’s near un-affordable.
Energy Consumption
Blockchain networks need a lot of energy to function. Equal to an entire country. Efforts are there to make it energy efficient. Which still remains a great concern for long-term sustainability.
Security
Blockchain architecture is distinct. Some are less secure than others. The decentralized ones are more vulnerable. It leaves all public blockchains at risk of 51% attack.
Public Perception
People don’t trust blockchain as a conventional solution. The majority think that it won’t last for long.
Integration With Legacy System
Organizations may have to rebuild from scratch. As it’s impossible to integrate blockchain with their legacy system.
Identifying A Good Use Case Of Blockchain
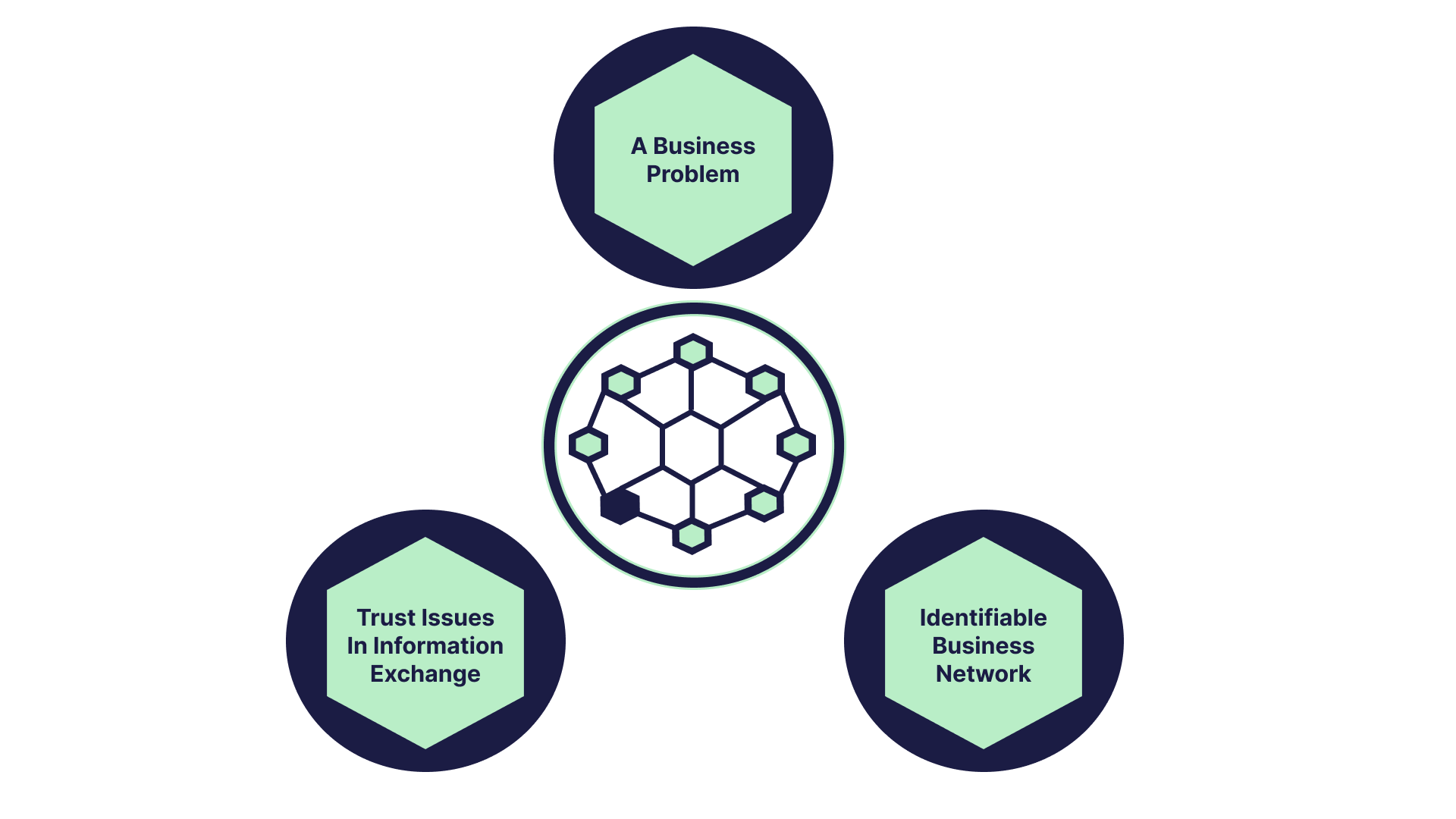
A good use case of blockchain should have the following:
1. A Business Problem That Blockchain Can Solve
Some notable blockchain features are
- Decentralization
- Immutability
- Transparency
- Security
- Efficiency
- Traceability, etc.
Solving business problems in various industries.
2. Identifiable Business Network
An identifiable business network offers increased security, efficiency, and transparency. All network transactions are visible to participants. Improving transparency and reducing the chance of fraud.
3. Trust Issues in Information Exchange
Transactions on the blockchain are secure and transparent. Reducing lack of confidence in information transmission.
Ways Blockchain Can Be & Is Being Used
Blockchain is a versatile technology that can be used in a variety of industries. Let’s jump into — how blockchain can be & is being used currently.
In Government Organization
The followings ways blockchain can be and in some is being used countries in
- To store and manage digital identities
- secure voting systems
- Track and trace government assets, etc
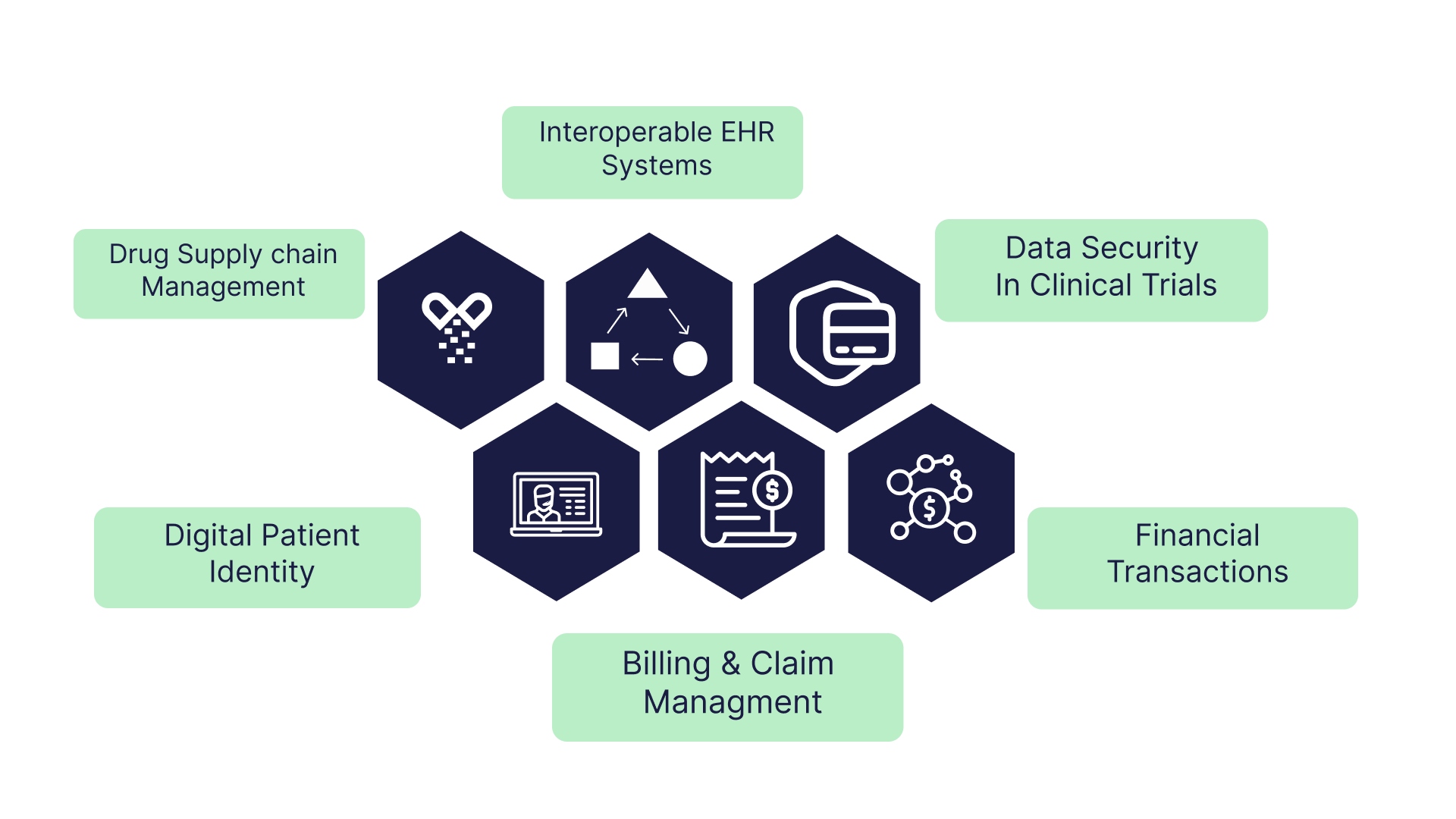
In Healthcare Industry
- Secure sharing of medical data
- Improved interoperability
- Medical Supply Chain Management
- Transparent Clinical Trials
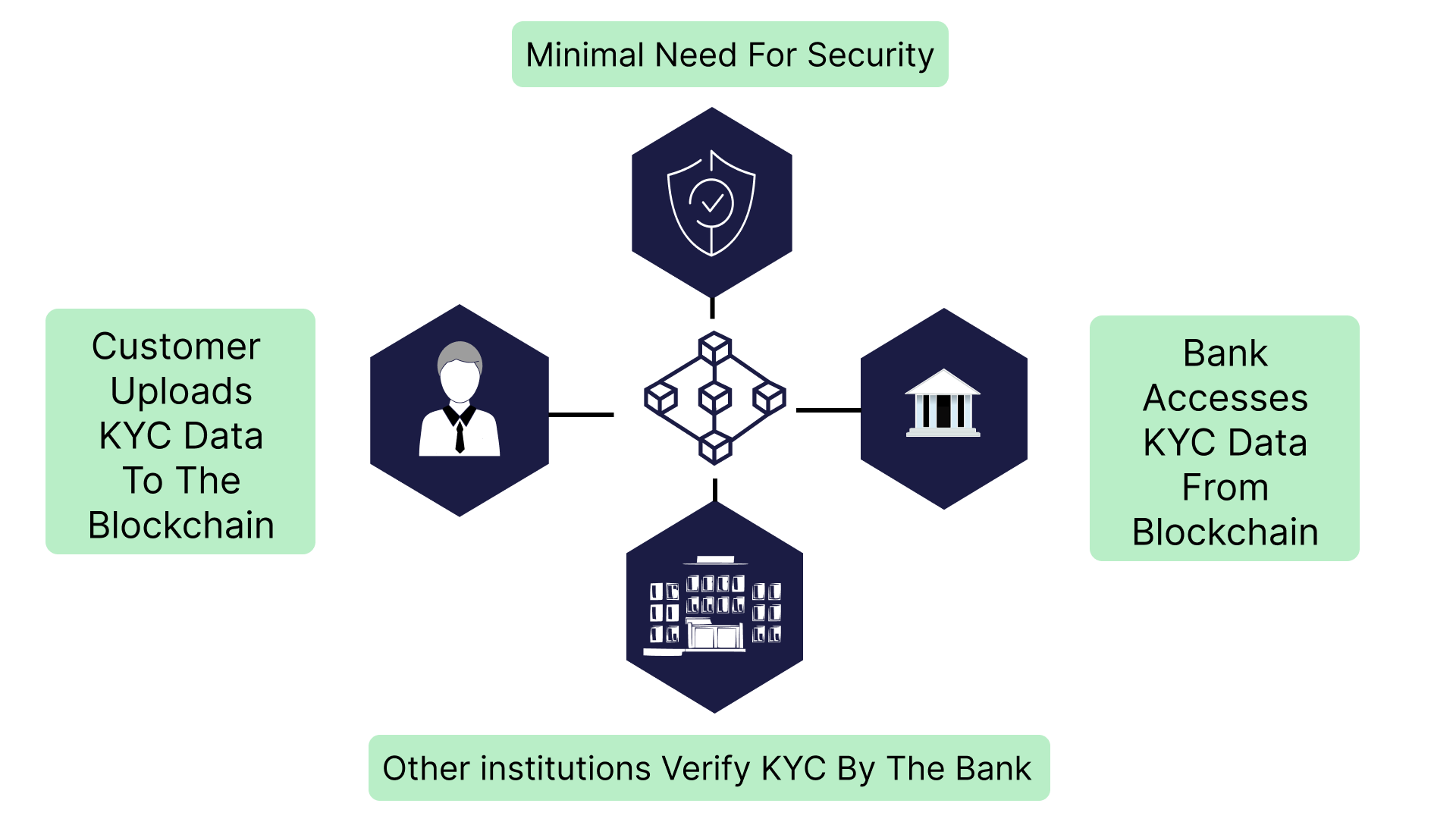
KYC (Know Your Customer)
Blockchain can be used to store & share customer data securely. Favoring compliance and regulatory purpose. Enabling secure transfer of eKYC verification stamps from one entity to another. Offering highly immutable and detailed audit trail on all actions on KYC files.
Trade Finance
Blockchain can be used to simplify processes reduce fraud, and enhance transparency and efficiency in global trade.
Mortgage Industry
Blockchain can reduce fraud, secure personal data, and secure transactions.
Energy Market
Media & Entertainment Industry
Blockchain can
- Secure and protect intellectual property rights
- Track and distribute royalties
- Enhance transparency in media transactions.
Gaming
Blockchain can enhance gaming experiences by
- Ensuring secure and transparent in-game asset trading
- Prevent cheating.
Tourism Industry
Blockchain can help the tourism industry in
- Customer loyalty Programs.
- Encouragement to Revisit Programs
- Simplify the process
- Secure access to reward data
- Secure booking, identity verification and reduce fraud
Supply Chain
Blockchain can improve the transparency and traceability of supply chain processes. Including recording the price, date, location, quality, and certification of the product.
IoT (Internet of Things)
Blockchain can enable secure and transparent communication. Allow secure data exchange among IoT devices. Also, reduce data breaches, and enhance privacy.
Real Estate Industry
Blockchain can improve the transparency and efficiency of real estate transactions, reduce fraud, and enhance the security of personal data.
Wrapping up
Blockchain technology could revolutionize many industries. However, there are challenges. The key to successful implementation is identifying good use cases. Its use cases are numerous. As we’ve seen in this blog, they extend beyond cryptocurrencies. And, we’re only scratching the surface of its potential.
Tags : Blockchain